| Prev | Next |
Auditing
Getting to know Auditing
Aspect |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Introducing Auditing |
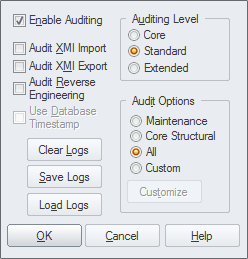
The Auditing feature can keep track of the changes to Requirements including what was changed, when it was changed and by whom. Auditing is by default disabled and must be enabled before the changes to requirements will be recorded. Once enabled it is a passive tool that silently records the changes to elements. It does not replace version control or baselines and in contradistinction to these tools it can not be used to return to a previous state of the model. Change management, governance and quality control are all aided by the use of Auditing.
|
|
Where to find Auditing |
|
|
Use of Auditing |
Auditing can be used to track what was changed in a model, who changed it and when. There are a number of modes and a repository administrator can use the settings to specify what is recorded in the audit. While a baseline can be used to show the difference between a model and a snapshot at a point in time, the Auditing tool records each individual change; it can not, however, be used to revert to a previous state. |
|
Options for Auditing |
There is a wide range of settings to configure auditing, starting with enabling or disabling the settings that determine which elements have an audit trail and the level of detail recorded. Audit logs can be exported from the repository to increase performance.
|
|
Learn more about Auditing |