| Prev | Next |
Logical Data Model
Logical data models help to define the detailed structure of the data elements in a system and the relationships between data elements. They refine the data elements introduced by a Conceptual data model and form the basis of the Physical data model. In Enterprise Architect, a Logical data model is typically represented using the UML Class notation.
Example
This is a simple example of a Logical data model:
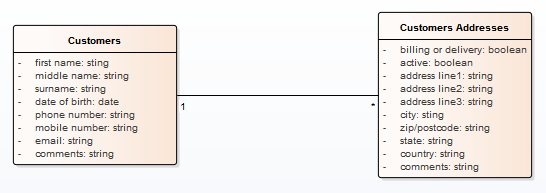
Note that the data elements 'Customers' and 'Customers Addresses' contain UML attributes; the names and generic data types to remain platform-independent. Platform-specific data types and other meta-data that relate to a specific DBMS implementation are defined by the Physical data model.
Learn more

